Coronary Angiography
A coronary angiogram is a procedure that uses X-ray imaging to see your heart's blood vessels. The test is generally done to see if there's a restriction in blood flow going to the heart. Coronary angiograms are part of a general group of procedures known as heart (cardiac) catheterizations
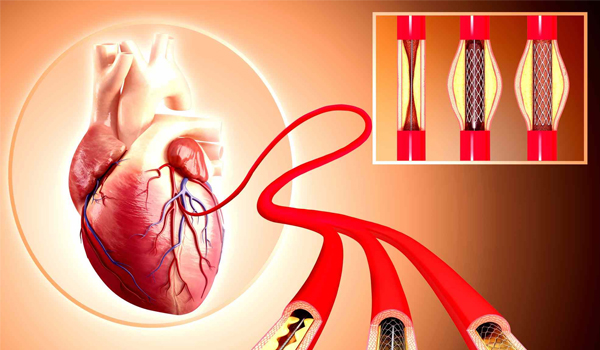
Coronary Angioplasty
A coronary angioplasty is a procedure used to widen blocked or narrowed coronary arteries (the main blood vessels supplying the heart). The term "angioplasty" means using a balloon to stretch open a narrowed or blocked artery.
- Primary angioplasty
- Elective Angioplasty
Coronary Imaging
Coronary calcium scoring/screening – This test uses a CT scan to take an image the heart, which looks for calcium deposits within the coronary arteries. Calcium is not present in normal coronary arteries and when present is a sign of atherosclerosis.
- IVUS
- OCT
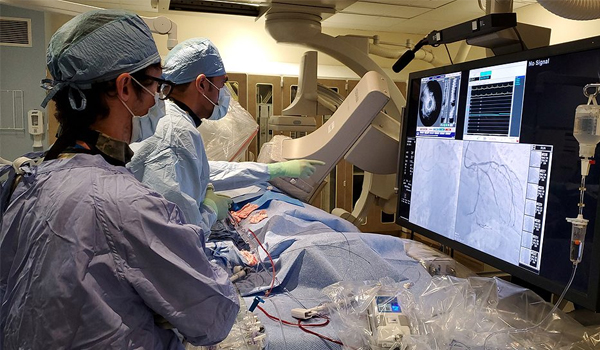
Intervention Cardiology
Interventional cardiology is a non-surgical option which uses a small, flexible tube called a catheter to repair damaged or weakened vessels, narrowed arteries, or other affected parts of the heart structure.
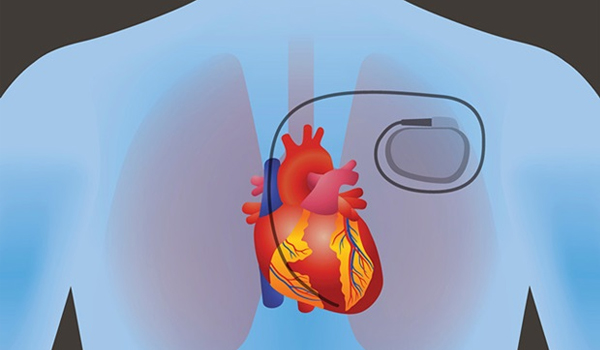
Pacemaker Implantation
The generator is usually placed under the skin near the collarbone on the left side of the chest. The generator is attached to a wire that's guided through a blood vessel to the heart. The procedure usually takes about an hour, and most people are able to leave hospital on the same day or a day after surgery.
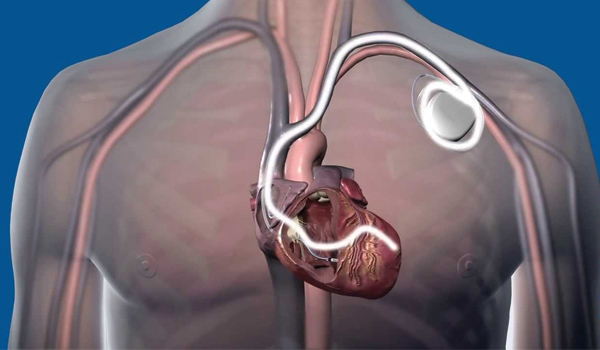
AICD implantation
Automatic implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (AICD) is a costly but effective treatment modality for the prevention of sudden cardiac death (SCD).
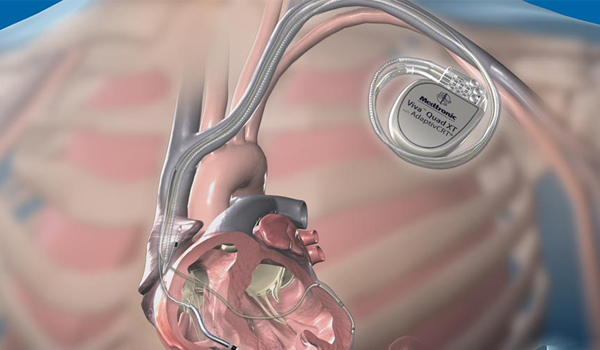
CRT
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) uses a device called a biventricular pacemaker — also called a cardiac resynchronization device — that sends electrical signals to both lower chambers of the heart (right and left ventricles).